Imagine a world where diseases are predicted and prevented before they even have a chance to threaten your health. Thanks to the incredible advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), this dream is becoming a reality. AI has the potential to revolutionize healthcare, allowing doctors and scientists to detect early signs of diseases and implement preventative measures. This groundbreaking technology has the potential to save countless lives and transform the way we approach healthcare. The question remains: can AI truly predict and prevent diseases? Let’s explore the fascinating capabilities of AI in the realm of healthcare.

The Role of AI in Disease Prevention
In recent years, the advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) technology has revolutionized many industries, and healthcare is no exception. AI has the potential to play a crucial role in disease prevention, ranging from the early detection of diseases to personalized medicine. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, deep learning networks, natural language processing, big data analytics, and the internet of medical things, AI can significantly improve disease prevention strategies. In this article, we will explore the various applications of AI in disease prevention, the advancements in AI technology, the challenges and limitations faced, success stories, and the future of AI in disease prevention.
Early Detection of Diseases
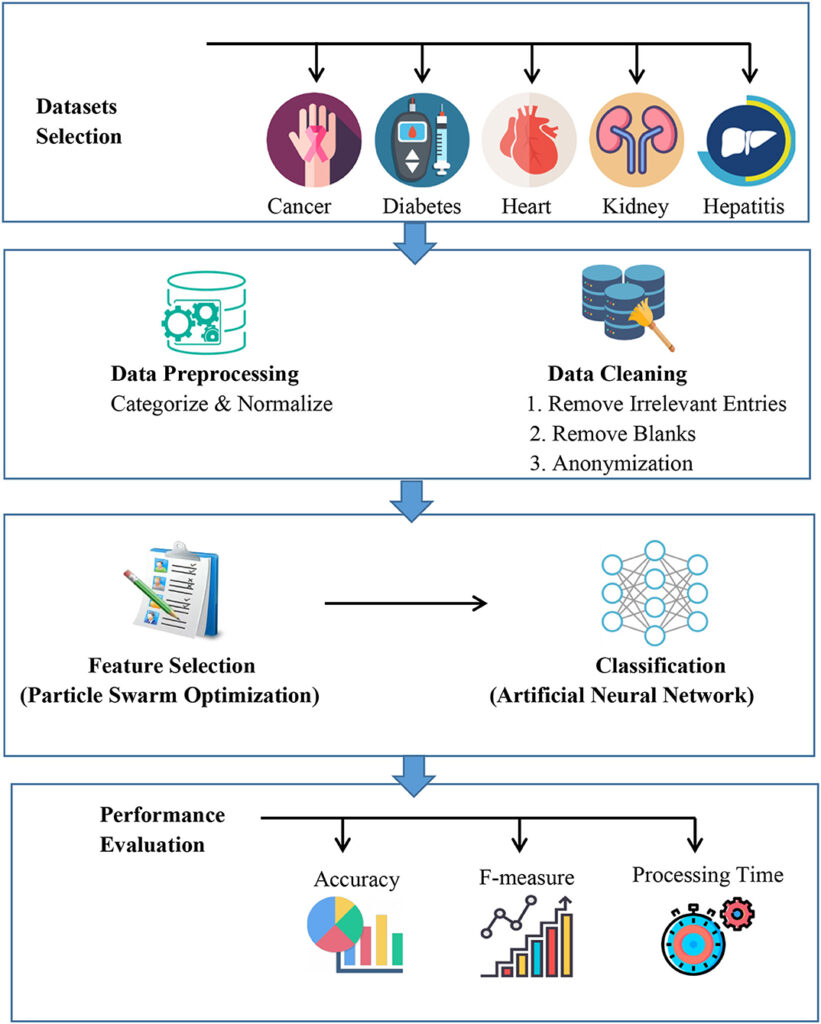
One of the key areas where AI excels in disease prevention is the early detection of diseases. Machine learning algorithms can analyze large amounts of data, including medical records, genetic information, and lifestyle factors, to identify patterns that may indicate the presence of a disease. By analyzing this data, AI-powered systems can identify potential risk factors and provide early warnings for diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. This early detection enables healthcare professionals to intervene at an early stage, increasing the chances of successful treatment and reducing the burden on patients and the healthcare system.
Identification of Disease Patterns
Another application of AI in disease prevention is the identification of disease patterns. By analyzing large datasets, AI algorithms can identify patterns and correlations in disease occurrence, allowing healthcare professionals to better understand the underlying causes and risk factors. This information can then be used to develop targeted prevention strategies, such as public health campaigns, lifestyle interventions, and genetic screening programs. By proactively addressing the factors that contribute to disease, AI can help reduce the overall disease burden and improve population health.
Prediction of Disease Outbreaks
AI can also be utilized to predict disease outbreaks, enabling timely interventions and resource allocation. By analyzing various data sources, including social media, satellite imagery, and healthcare records, AI algorithms can identify early indicators of an outbreak and predict its spread. For instance, AI-powered systems can analyze tweets and news reports to detect mentions of symptoms and monitor changes in disease activity. This early warning system allows public health officials to take immediate action, such as implementing quarantine measures, deploying medical resources, and alerting the public, thereby preventing further spread and minimizing the impact of the outbreak.
Personalized Medicine
AI has the potential to transform the field of medicine by enabling personalized treatment plans. By analyzing an individual’s genetic information, medical history, lifestyle factors, and treatment outcomes, AI algorithms can develop personalized treatment recommendations. For example, in cancer treatment, AI can analyze the genetic profile of a tumor and identify the most effective treatment options for that specific patient. This personalized approach maximizes treatment efficacy while minimizing side effects, leading to better patient outcomes. Personalized medicine enabled by AI has the potential to revolutionize the way diseases are treated, providing targeted therapies that are tailored to an individual’s unique biology.
Preventive Measures
In addition to early detection and personalized medicine, AI can assist in developing preventive measures to reduce the risk of disease. By analyzing large datasets and identifying risk factors, AI algorithms can recommend preventive actions such as lifestyle modifications, vaccinations, and regular screenings. For instance, AI-powered systems can analyze an individual’s lifestyle choices, such as diet, exercise, and sleep patterns, and provide tailored recommendations to reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases. By empowering individuals with personalized preventive measures, AI can significantly reduce the overall disease burden and improve population health.
Advancements in AI Technology
The rapid advancements in AI technology have paved the way for its widespread application in disease prevention. Here are some of the key advancements that have contributed to the effectiveness and capabilities of AI in the healthcare industry.
Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms are at the heart of AI-powered systems. These algorithms continuously learn from data, improve their performance, and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. In the context of disease prevention, machine learning algorithms analyze large datasets to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and make recommendations. By constantly learning and adapting, these algorithms can improve their accuracy and effectiveness over time.
Deep Learning Networks
Deep learning networks, a subset of machine learning, have proven to be highly effective in handling complex and unstructured data. These networks are composed of multiple layers of interconnected artificial neurons, simulating the structure and function of the human brain. Deep learning networks excel in tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and pattern detection. In disease prevention, deep learning networks can analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, to detect abnormalities and aid in diagnosis.
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a branch of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and human language. NLP enables computers to understand, interpret, and respond to human language in a meaningful way. In the context of disease prevention, NLP can be used to analyze medical records, research literature, and patient-reported data. By extracting relevant information from these unstructured sources, NLP-powered systems can enhance disease surveillance, support clinical decision-making, and improve patient outcomes.
Big Data Analytics
The advent of big data has provided an unprecedented opportunity for AI in disease prevention. Big data analytics refers to the process of analyzing large and complex datasets to uncover patterns, trends, and insights. In the context of disease prevention, big data analytics can integrate diverse sources of data, such as electronic health records, genomics data, and environmental data, to provide a comprehensive understanding of disease risk factors and outcomes. By harnessing the power of big data analytics, AI can provide valuable insights that can inform preventive strategies and improve patient care.
Internet of Medical Things
The internet of medical things (IoMT) refers to the network of interconnected medical devices, sensors, and wearables that collect and transmit health-related data. AI can leverage this vast amount of data to gain insights into individual health and enable personalized interventions. For example, wearable devices can continuously monitor an individual’s vital signs and activity levels, and AI algorithms can analyze this data to identify potential health risks and recommend appropriate interventions. The IoMT, combined with AI, has the potential to revolutionize disease prevention by enabling real-time monitoring and interventions.
Applications of AI in Disease Prevention
With its impressive capabilities, AI is being applied to a wide range of areas in disease prevention. Here are some of the key applications where AI is making a significant impact.
Detection and Diagnosis of Cancer
Cancer is a leading cause of mortality worldwide, and early detection is critical for successful treatment. AI algorithms can analyze medical images, such as mammograms and pathology slides, to detect cancerous lesions with high accuracy. By assisting radiologists and pathologists in the interpretation of images, AI-powered systems can improve the efficiency and accuracy of cancer diagnosis. Furthermore, AI can analyze genetic data to identify individuals at high risk of developing cancer, enabling targeted screening and prevention strategies.
Monitoring Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and respiratory diseases, require continuous monitoring and management. AI-powered systems can analyze data from wearable devices, such as glucose meters and heart rate monitors, to track disease progression and provide personalized recommendations for disease management. By continuously monitoring key parameters and analyzing trends, AI can help individuals manage their chronic diseases effectively and avoid complications.
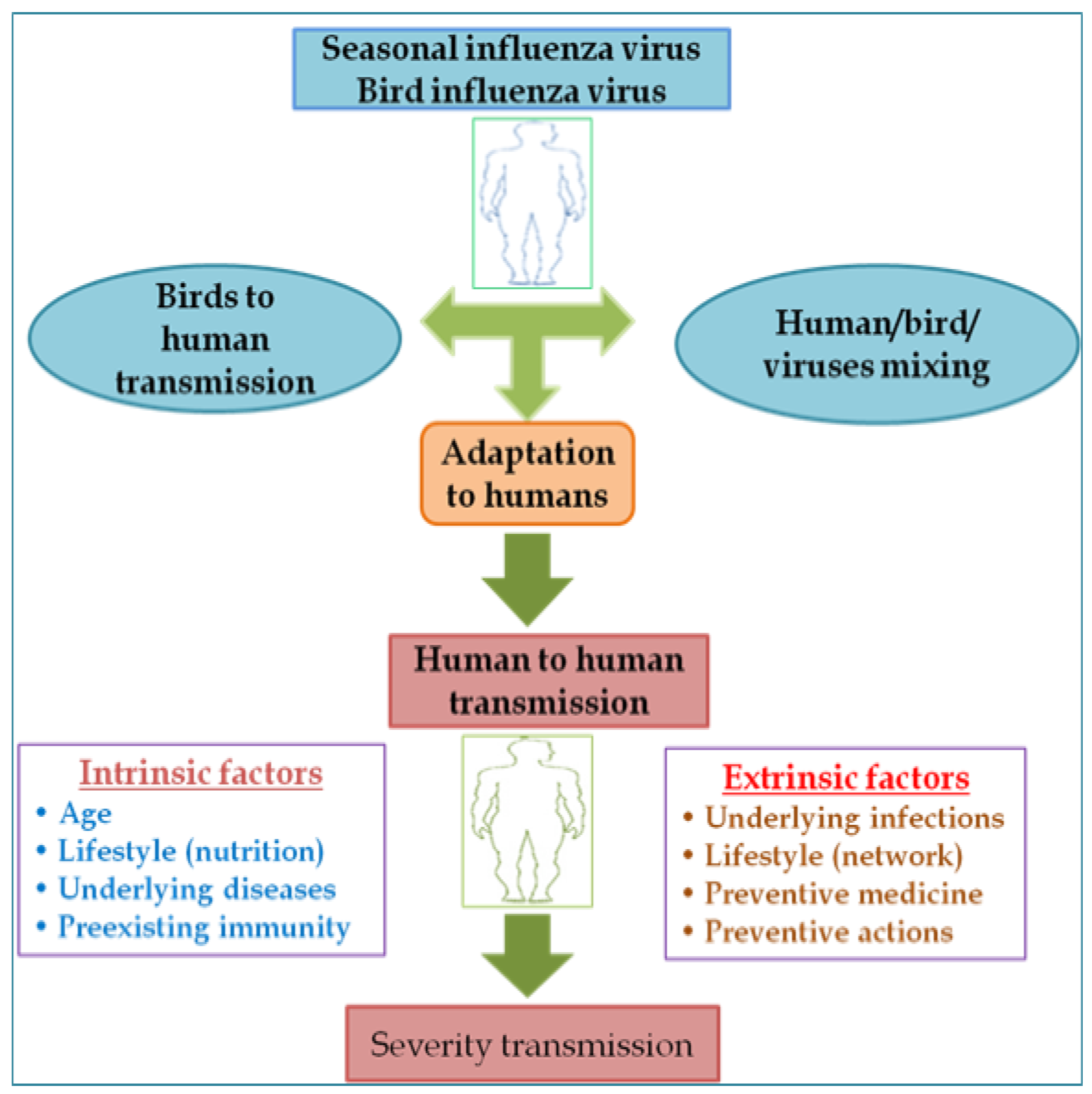
Tracking Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases, such as influenza, Ebola, and COVID-19, pose significant challenges to public health. AI can aid in the tracking and surveillance of infectious diseases by analyzing diverse data sources, such as social media, temperature data, and travel patterns. By monitoring disease activity, identifying outbreak hotspots, and predicting disease spread, AI-powered systems can assist public health officials in making informed decisions and implementing timely interventions to control the spread of infectious diseases.
Drug Discovery and Development
Traditional drug discovery and development processes are time-consuming and expensive. AI has the potential to accelerate and optimize these processes by analyzing large datasets and predicting drug properties and interactions. By simulating and modeling the behavior of molecules, AI algorithms can screen potential drug candidates and prioritize those with the highest likelihood of success. Furthermore, AI can assist in the repurposing of existing drugs for new indications, reducing the time and cost required for drug development.
Genomic Medicine
Genomic medicine, which focuses on the use of genetic information to inform healthcare decisions, is an area where AI can make a significant impact. AI algorithms can analyze large genomic datasets to identify disease-associated genetic variants and predict an individual’s risk of developing certain diseases. This information can then be used to inform personalized prevention strategies, such as targeted screening, lifestyle modifications, and preventive medications. By integrating genomics and AI, healthcare professionals can provide individualized care and interventions based on a person’s unique genetic makeup.
Challenges and Limitations
While AI shows great promise in disease prevention, there are several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed.
Data Privacy and Security
The use of AI in healthcare involves handling sensitive and personal data, raising concerns about data privacy and security. Protecting patient privacy and ensuring the security of medical data are paramount. Robust data protection mechanisms, secure storage solutions, and strict access controls must be in place to address these concerns.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical implications of AI in disease prevention are complex and require careful consideration. For instance, the use of AI algorithms in decision-making processes raises questions about transparency, accountability, and bias. It is essential to ensure the fairness, transparency, and ethical use of AI algorithms to avoid any potential harm or discrimination.
Reliability and Accuracy
The reliability and accuracy of AI algorithms are critical for their effective use in disease prevention. AI algorithms learn from data, and if the data is biased, incomplete, or of poor quality, it can negatively impact the performance of the algorithms. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that AI algorithms are trained on high-quality, diverse, and representative datasets to ensure their reliability and accuracy.
Integration with Healthcare Systems
Integrating AI-powered systems into existing healthcare systems can be challenging. Healthcare organizations often have complex IT infrastructures, data silos, and interoperability issues, which can hinder the seamless integration and utilization of AI. Collaboration between AI developers and healthcare professionals is essential to overcome these challenges and ensure the effective implementation of AI in disease prevention.
Cost and Accessibility
The cost of implementing AI technology can be a barrier to its widespread adoption. AI-enabled systems often require significant investment in infrastructure, data storage, computing power, and specialized personnel. Ensuring the accessibility and affordability of AI-powered solutions is crucial to ensure that they reach all populations and contribute to reducing health disparities.
Success Stories in Disease Prevention
Despite the challenges, AI has already demonstrated remarkable success in disease prevention. Here are some notable success stories.
Epidemics and Outbreaks
During the Ebola outbreak in West Africa in 2014, AI algorithms were used to analyze social media data and identify areas at high risk of disease spread. This information was then used to prioritize prevention and control efforts, leading to a more targeted and effective response.
Cancer Detection
AI algorithms have shown impressive performance in the detection of cancer. For example, a deep learning network developed by Google’s DeepMind demonstrated higher accuracy than human radiologists in identifying breast cancer from mammograms. This breakthrough has the potential to improve early detection rates and save lives.
Chronic Disease Management
AI-powered systems have been successfully used in the management of chronic diseases. For instance, wearable devices equipped with AI algorithms have helped individuals with diabetes monitor their blood glucose levels, maintain healthy lifestyles, and avoid complications. These personalized interventions have shown positive outcomes in disease management and patient well-being.
Drug Development
The application of AI in drug development has yielded promising results. For example, AI algorithms have been used to identify potential drug candidates for the treatment of rare genetic diseases, significantly speeding up the discovery process. AI-powered drug discovery platforms are also being used to repurpose existing drugs for new indications, providing new treatment options at a fraction of the time and cost.
Genetic Disease Prevention
AI has shown great potential in the prevention of genetic diseases. By analyzing genetic data, AI algorithms can identify individuals at high risk of developing genetic conditions and inform them about available preventive measures. This personalized approach has the potential to significantly reduce the burden of genetic diseases and improve overall health outcomes.
The Future of AI in Disease Prevention
The future of AI in disease prevention looks promising, with several exciting developments on the horizon.
Precision Medicine
As our understanding of genetics and disease mechanisms improves, AI will play a crucial role in enabling precision medicine. AI algorithms will analyze vast genomic datasets, clinical data, and lifestyle information to develop highly personalized treatment plans. Precision medicine will allow healthcare professionals to tailor interventions to an individual’s unique genetic makeup, improving treatment outcomes and minimizing side effects.
Real-Time Disease Surveillance
AI-powered systems will continue to enhance real-time disease surveillance and early warning systems. By integrating diverse data sources, including social media, sensor data, and healthcare records, AI algorithms will be able to detect disease outbreaks, monitor disease activity, and predict disease spread with greater accuracy. Real-time disease surveillance will enable public health officials to take immediate action and prevent the rapid spread of infectious diseases.
AI as a Diagnostic Tool
AI algorithms will increasingly be used as diagnostic tools, aiding healthcare professionals in making accurate and timely diagnoses. For example, AI algorithms can analyze medical images, pathology slides, and genetic data to assist in the diagnosis of complex diseases. By providing objective and evidence-based support, AI algorithms can improve diagnostic accuracy, reduce diagnostic errors, and enable more targeted treatment decisions.
Global Collaboration
The future of AI in disease prevention will rely heavily on global collaboration and sharing of data and expertise. By establishing international collaborations, healthcare organizations, researchers, and AI developers can pool their resources, share knowledge, and develop robust AI-powered solutions. Global collaboration will enable the development of comprehensive disease prevention strategies that transcend geographical boundaries and have a global impact.
Empowering Healthcare Professionals
AI technology will continue to empower healthcare professionals by providing them with actionable insights and decision support. AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of data, extract relevant information, and present it in a user-friendly manner. This data-driven approach will enable healthcare professionals to make evidence-based decisions, enhance patient care, and improve health outcomes.
Conclusion
AI has the potential to revolutionize disease prevention by enabling early detection, personalized medicine, and preventive strategies. With advancements in machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, big data analytics, and the internet of medical things, AI is becoming increasingly sophisticated and effective in addressing the challenges of disease prevention. While there are challenges and limitations to overcome, the success stories and future prospects of AI in disease prevention are promising. By harnessing the power of AI and ensuring its ethical and responsible use, we can make significant strides in reducing the burden of diseases and improving population health.